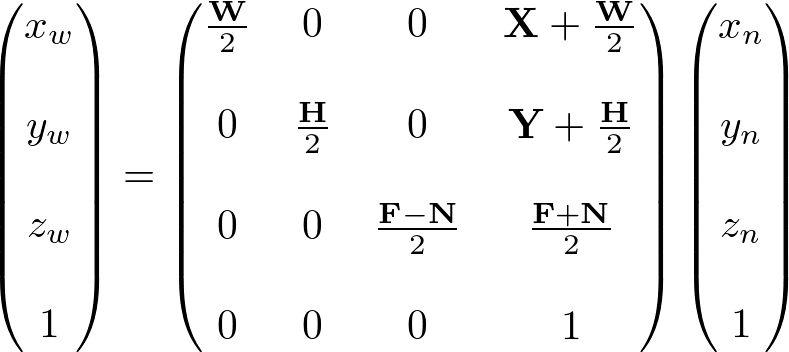OpenGL Viewport Transform
Related Topics: OpenGL Transformation, OpenGL Projection Matrix
Overview
The last step of vertex operations in OpenGL is viewport transform converting the normalized device coordinates (NDC) to window (screen) coordinates in order to map the NDC to the 2D screen. Note that the window coordinates still keep the Z coordinate for the depth testing during the fragment operations later.
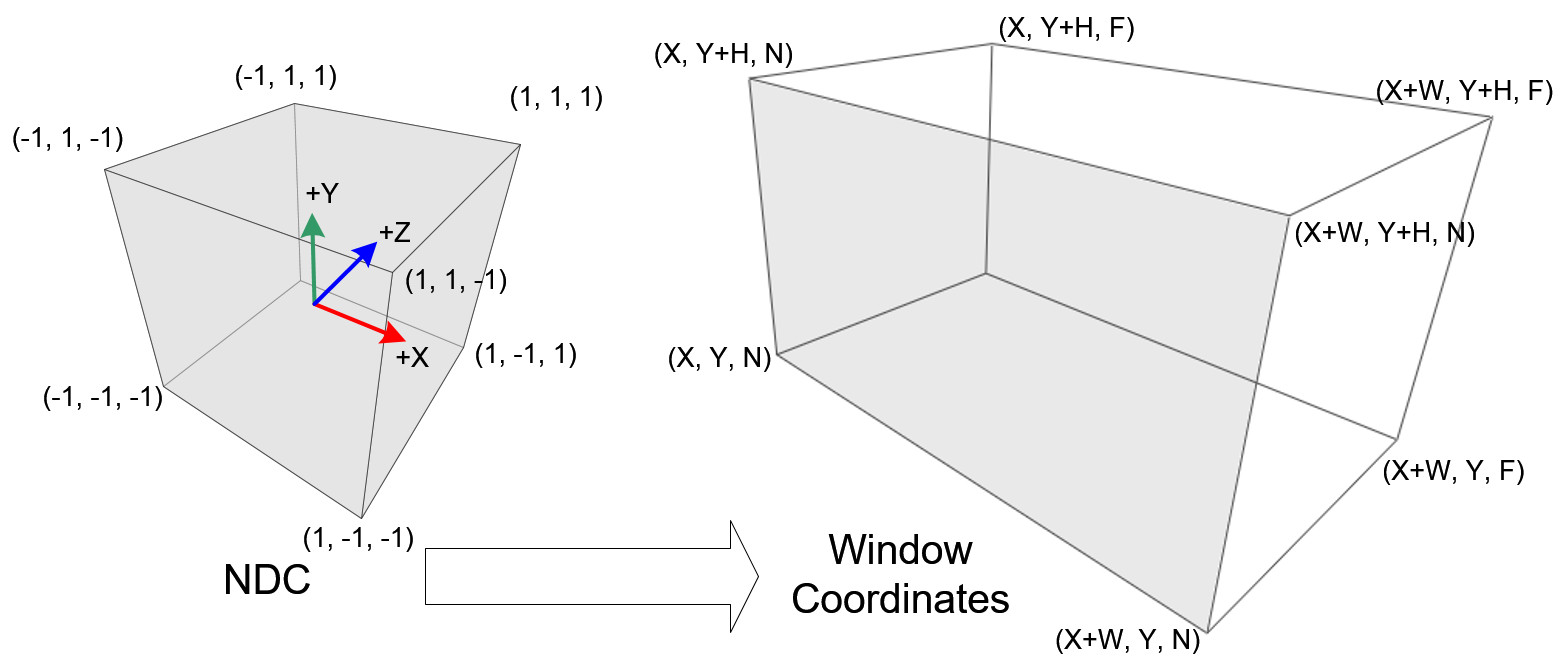
OpenGL provides 2 functions to specify the 2D rectangle of the rendering screen and the depth range. glViewport() is to set the viewport of the window, and glDepthRange()/glDepthRangef() is to map the depth values from NDC to window coordinates.
glViewport(X, Y, W, H)
glDepthRangef(N, F)
The parameters of these functions are;
- X: the left corner of the viewport
- Y: the bottom corner of the viewport
- W: the width of the viewport
- H: the height of the viewport
- N: the near clipping value, 0 by default
- F: the far clipping value, 1 by default
NDC to Window Coordinates
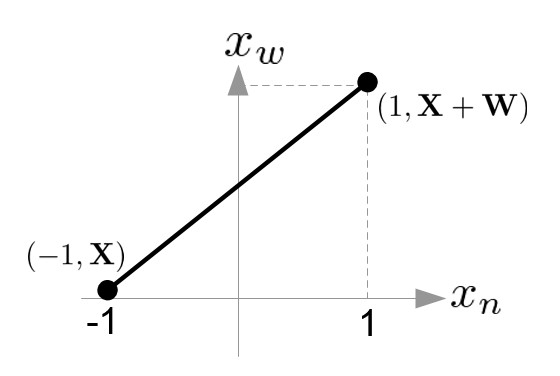
The viewport transform from NDC, ![]() to window coordinates,
to window coordinates, ![]() is solving a line equation with 2 known points.
is solving a line equation with 2 known points.
- X-Axis: (-1, X) and (1, X+W)
- Y-Axis: (-1, Y) and (1, Y+H)
- Z-Axis: (-1, N) and (1, F)
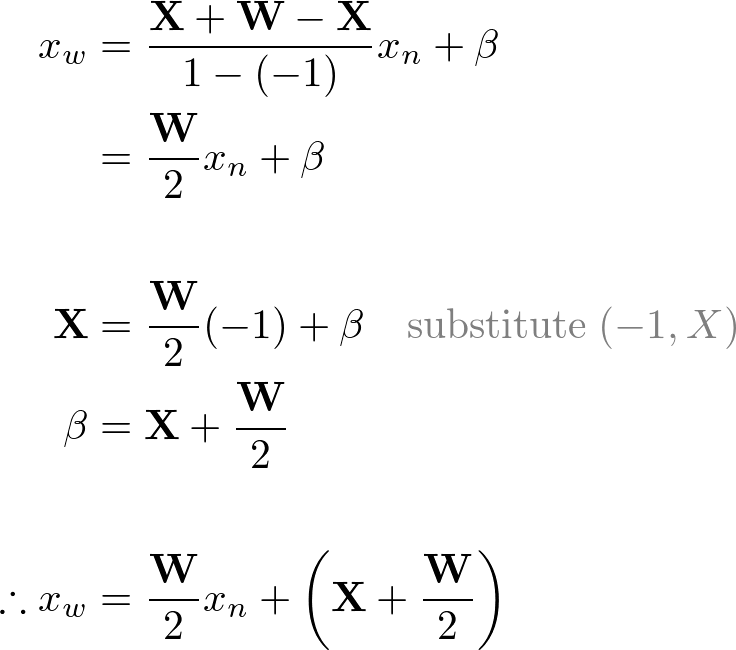
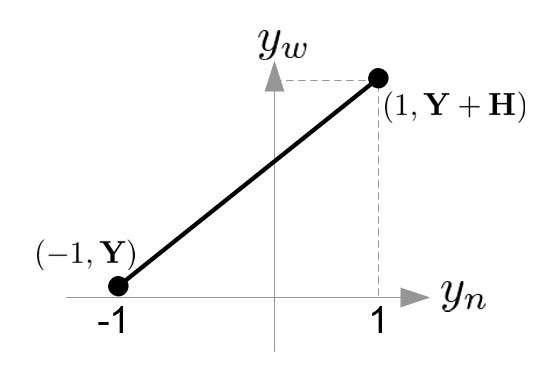
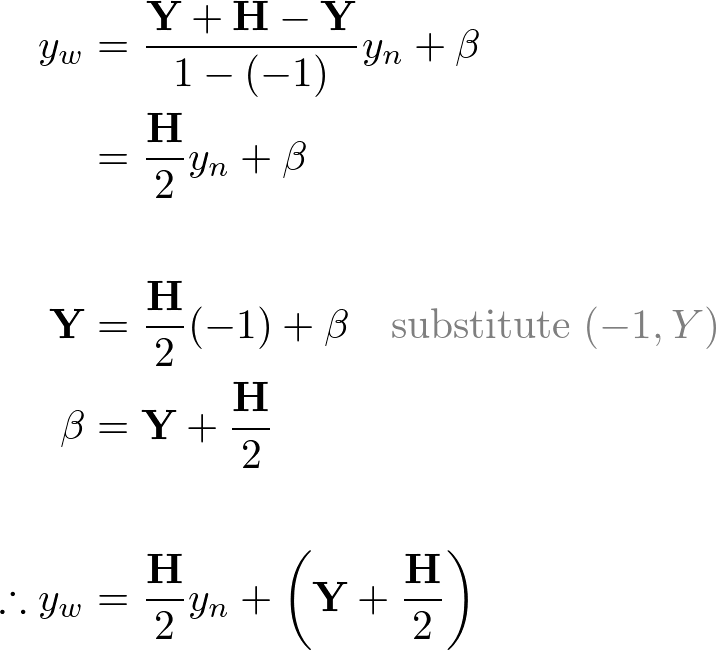
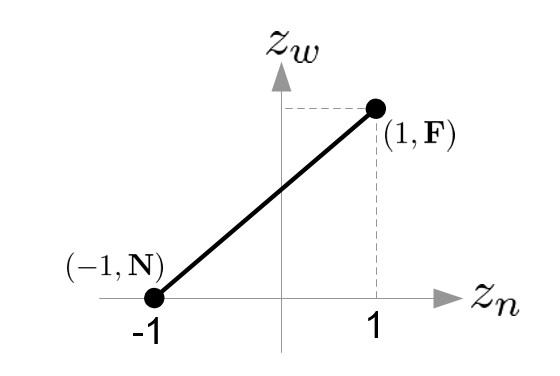
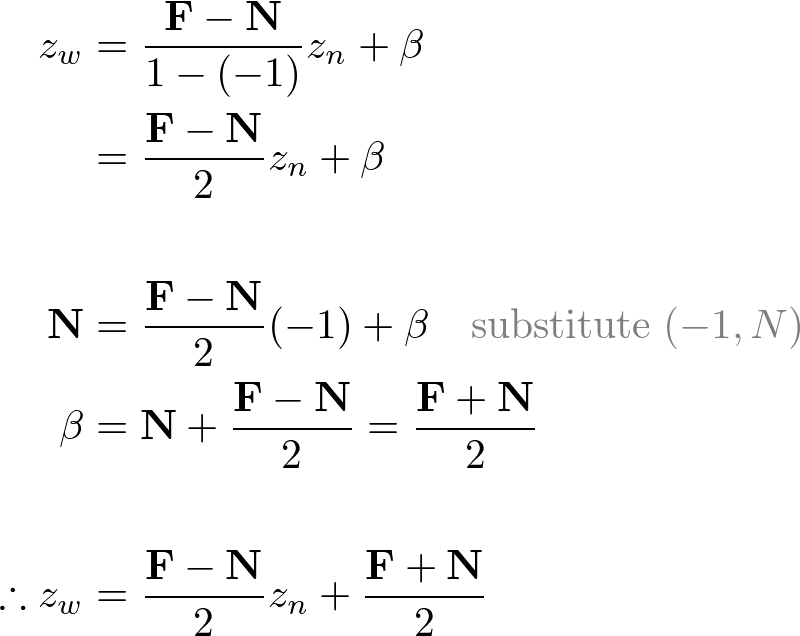
Therefore, the conversion formula for all 3 coordinates together;
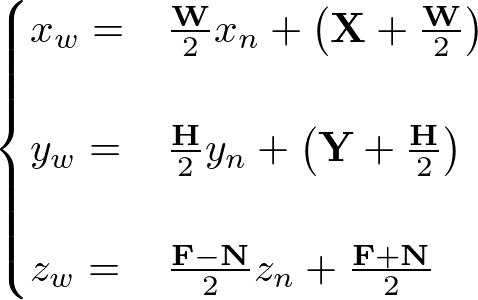
Or, the equivalent 4x4 viewport transform matrix is;